Last Updated on April 26, 2024 by Ecologica Life
The Mars ocean theory predicts that almost a third of its surface was formerly covered by water. In 2013 NASA reported that the curiosity rover what used to be a freshwater lake. Now the planet is just a dusty, parched wasteland. The only water on the surface is mostly in the polar ice caps and a small amount as water vapour in the atmosphere.

Under the Martian surface, a vast water body likely to be in water ice form, has been found. This could be ideal for future astronauts if they could get access to this water. Furthermore, the presence of water on Mars could indicate that life once existed there, or could in some form, exist today.
The question is, why isn’t Mars a blue planet anymore like the Earth is today?
The loss of the magnetosphere on Mars
About four billion years ago. Mars’s magnetic field (magnetosphere) began to severely weaken. The processes behind the loss of Mars’s magnetosphere are complex and not completely understood but more can be read at universetoday.
For a rocky planet to lose its magnetosphere will have grave consequences for life on that planet. On Earth, our magnetosphere keeps us safe from solar winds and dangerous cosmic rays. Due to this, current day Mars may have no life at all. Although it is possible that microbial life has survived on the red planet but no direct evidence of this has been found yet.
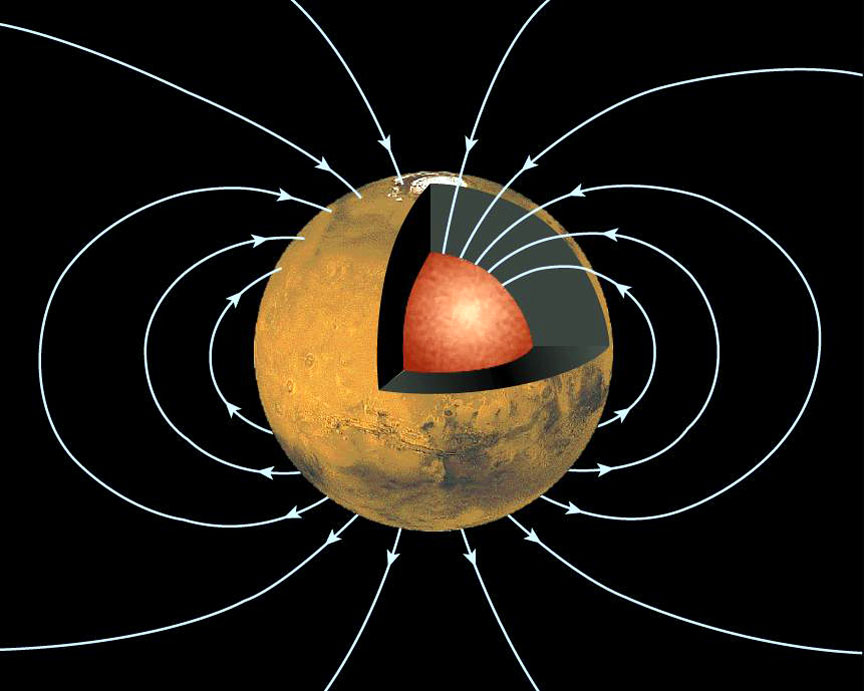
Once Mars lost its magnetosphere, it no longer had its blanket of protection from these dangerous solar winds. Thus, the solar winds stripped the planet of the atmosphere. After Mars lost its atmosphere, liquid water on the surface dried up. Scientists are still unsure as to how or why the water in liquid state on Mars dried up, although some interesting theories have been proposed.
Could the magnetosphere on Mars be revived?
The answer is no, and yes. Earth’s magnetic field is produced by a dynamo effect of molten iron under high pressure in the planet’s core. The interior of Mars is smaller and cooler, and we can’t just simply “start it up” to create a magnetic dynamo. However, as a 2021 study demonstrated, an artificial magnetic field could potentially work.
It has been proposed that, shooting a strong flow of charged particles around the orbit, using its moon Phobos, could in theory work.
This is important to consider if humans want to one day terraform Mars, or at least to put humans on Mars, as Elon Musk plans to do by 2040. A stable magnetic field would protect those individuals from the hostile solar winds and cosmic rays.
These bold ideas are futuristic in the least, but if achieved, life could be given a second chance to thrive on another planet. Imagine that future generations might be able to fly to Mars in space travel that is as easy as flying somewhere in a plane today? Life on Mars would initially be very similar to Earth but after millions of years it may look quite different life on Earth. How Bizarre!
Will Earth maintain its magnetosphere?
Earth for the most part has a stable magnetosphere and will not lose it the way Mars did, at least for a billion years. However, it is true that the Earth’s magnetic field flips periodically – up to 100 times in the past 20 million years. When this happens, magnetic north becomes magnetic south and vice versa. We know this because when the magnetic field reversals happen, fossilised magnetisation occurs, leaving remains of magnetic particles trapped in minerals for scientists to examine.
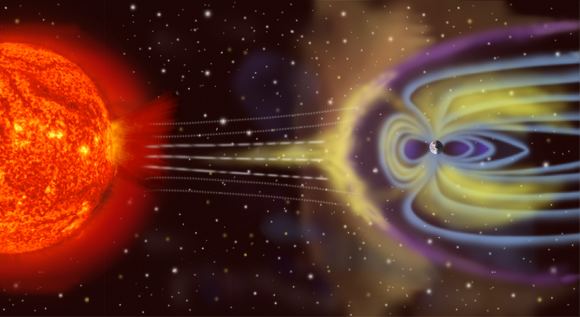
The next flip may occur within the next couple millennia. When this occurs, space stations may lose their ability to communicate with earth and communication systems worldwide could be affected. Prolonged exposure to cosmic rays would increase the mutation rate of living cells, leading to cancers in animals. Depending on how long the field flip might take, we will have to prepare accordingly.
What do you think about this article? Leave us a comment or suggestion and we will get back to you as soon as we can.







